현재 위치
홈상품상세정보
Overview
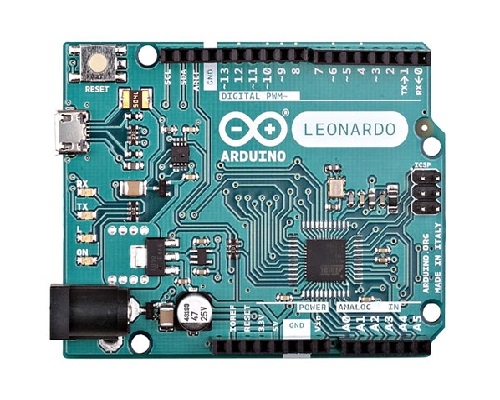
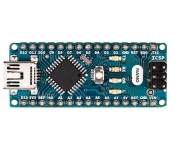
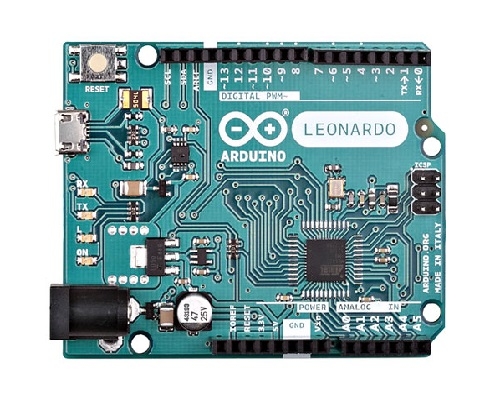
The Arduino Leonardo is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega32u4 (datasheet). It has 20 digital input/output pins (of which 7 can be used as PWM outputs and 12 as analog inputs), a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a micro USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
The Leonardo differs from all preceding boards in that the ATmega32u4 has built-in USB communication, eliminating the need for a secondary processor. This allows the Leonardo to appear to a connected computer as a mouse and keyboard, in addition to a virtual (CDC) serial / COM port. It also has other implications for the behaviour of the board.
Summary
Microcontroller
ATmega32u4
Operating Voltage
5V
Input Voltage (recommended)
7-12V
Input Voltage (limits)
6-20V
Digital I/O Pins
20
PWM Channels
7
Analog Input Channels
12
DC Current per I/O Pin
40 mA
DC Current for 3.3V Pin
50 mA
Flash Memory
32 KB (ATmega32u4) of which 4 KB used by bootloader
SRAM
2.5 KB (ATmega32u4)
EEPROM
1 KB (ATmega32u4)
Clock Speed
16 MHz
Length
68.6 mm
Width
53.3 mm
Weight
20g
Microcontroller | ATmega32u4 |
Operating Voltage | 5V |
Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V |
Input Voltage (limits) | 6-20V |
Digital I/O Pins | 20 |
PWM Channels | 7 |
Analog Input Channels | 12 |
DC Current per I/O Pin | 40 mA |
DC Current for 3.3V Pin | 50 mA |
Flash Memory | 32 KB (ATmega32u4) of which 4 KB used by bootloader |
SRAM | 2.5 KB (ATmega32u4) |
EEPROM | 1 KB (ATmega32u4) |
Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
Length | 68.6 mm |
Width | 53.3 mm |
Weight | 20g |
Schematic & Reference Design
Power
The Arduino Leonardo can be powered via the micro USB connection or with an external power supply. The power source is selected automatically.
External (non-USB) power can come either from an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be connected by plugging a 2.1mm center-positive plug into the board's power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in the Gnd and Vin pin headers of the POWER connector.
The board can operate on an external supply of 6 to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may supply less than five volts and the board may be unstable. If using more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the board. The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
The power pins are as follows:
- VIN. The input voltage to the Arduino board when it's using an external power source (as opposed to 5 volts from the USB connection or other regulated power source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying voltage via the power jack, access it through this pin.
- 5V. The regulated power supply used to power the microcontroller and other components on the board. This can come either from VIN via an on-board regulator, or be supplied by USB or another regulated 5V supply.
- 3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board regulator. Maximum current draw is 50 mA.
- GND. Ground pins.
- IOREF. The voltage at which the i/o pins of the board are operating (i.e. VCC for the board). This is 5V on the Leonardo.
The Arduino Leonardo can be powered via the micro USB connection or with an external power supply. The power source is selected automatically.
External (non-USB) power can come either from an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be connected by plugging a 2.1mm center-positive plug into the board's power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in the Gnd and Vin pin headers of the POWER connector.
The board can operate on an external supply of 6 to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may supply less than five volts and the board may be unstable. If using more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the board. The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
The power pins are as follows:
- VIN. The input voltage to the Arduino board when it's using an external power source (as opposed to 5 volts from the USB connection or other regulated power source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying voltage via the power jack, access it through this pin.
- 5V. The regulated power supply used to power the microcontroller and other components on the board. This can come either from VIN via an on-board regulator, or be supplied by USB or another regulated 5V supply.
- 3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board regulator. Maximum current draw is 50 mA.
- GND. Ground pins.
- IOREF. The voltage at which the i/o pins of the board are operating (i.e. VCC for the board). This is 5V on the Leonardo.
Memory
The ATmega32u4 has 32 KB (with 4 KB used for the bootloader). It also has 2.5 KB of SRAM and 1 KB of EEPROM (which can be read and written with the EEPROM library).
The ATmega32u4 has 32 KB (with 4 KB used for the bootloader). It also has 2.5 KB of SRAM and 1 KB of EEPROM (which can be read and written with the EEPROM library).
Input and Output
Each of the 20 digital i/o pins on the Leonardo can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive a maximum of 40 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by default) of 20-50 kOhms. In addition, some pins have specialized functions:
- Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data using the ATmega32U4 hardware serial capability. Note that on the Leonardo, the Serial class refers to USB (CDC) communication; for TTL serial on pins 0 and 1, use the Serial1 class.
- TWI: 2 (SDA) and 3 (SCL). Support TWI communication using the Wire library.
- External Interrupts: 3 (interrupt 0), 2 (interrupt 1), 0 (interrupt 2), 1 (interrupt 3) and 7 (interrupt 4). These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value. See the attachInterrupt() function for details.
- PWM: 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, and 13. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function.
- SPI: on the ICSP header. These pins support SPI communication using the SPI library. Note that the SPI pins are not connected to any of the digital I/O pins as they are on the Uno, They are only available on the ICSP connector. This means that if you have a shield that uses SPI, but does NOT have a 6-pin ICSP connector that connects to the Leonardo's 6-pin ICSP header, the shield will not work.
- LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off.
- Analog Inputs: A0-A5, A6 - A11 (on digital pins 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, and 12). The Leonardo has 12 analog inputs, labeled A0 through A11, all of which can also be used as digital i/o. Pins A0-A5 appear in the same locations as on the Uno; inputs A6-A11 are on digital i/o pins 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, and 12 respectively. Each analog input provides 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different values). By default the analog inputs measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and the analogReference() function.
There are a couple of other pins on the board:
AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference().
Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one on the board.
Each of the 20 digital i/o pins on the Leonardo can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive a maximum of 40 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by default) of 20-50 kOhms. In addition, some pins have specialized functions:
- Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data using the ATmega32U4 hardware serial capability. Note that on the Leonardo, the Serial class refers to USB (CDC) communication; for TTL serial on pins 0 and 1, use the Serial1 class.
- TWI: 2 (SDA) and 3 (SCL). Support TWI communication using the Wire library.
- External Interrupts: 3 (interrupt 0), 2 (interrupt 1), 0 (interrupt 2), 1 (interrupt 3) and 7 (interrupt 4). These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value. See the attachInterrupt() function for details.
- PWM: 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, and 13. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function.
- SPI: on the ICSP header. These pins support SPI communication using the SPI library. Note that the SPI pins are not connected to any of the digital I/O pins as they are on the Uno, They are only available on the ICSP connector. This means that if you have a shield that uses SPI, but does NOT have a 6-pin ICSP connector that connects to the Leonardo's 6-pin ICSP header, the shield will not work.
- LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off.
- Analog Inputs: A0-A5, A6 - A11 (on digital pins 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, and 12). The Leonardo has 12 analog inputs, labeled A0 through A11, all of which can also be used as digital i/o. Pins A0-A5 appear in the same locations as on the Uno; inputs A6-A11 are on digital i/o pins 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, and 12 respectively. Each analog input provides 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different values). By default the analog inputs measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and the analogReference() function.
There are a couple of other pins on the board:
AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference().
Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one on the board.
Communication
The Leonardo has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer, another Arduino, or other microcontrollers. The ATmega32U4 provides UART TTL (5V) serial communication, which is available on digital pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). The 32U4 also allows for serial (CDC) communication over USB and appears as a virtual com port to software on the computer. The chip also acts as a full speed USB 2.0 device, using standard USB COM drivers. On Windows, a .inf file is required. The Arduino software includes a serial monitor which allows simple textual data to be sent to and from the Arduino board. The RX and TX LEDs on the board will flash when data is being transmitted via the USB connection to the computer (but not for serial communication on pins 0 and 1).
A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the Leonardo's digital pins.
The ATmega32U4 also supports I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino software includes a Wire library to simplify use of the I2C bus. For SPI communication, use the SPI library.
The Leonardo appears as a generic keyboard and mouse, and can be programmed to control these input devices using the Keyboard and Mouse classes.
The Leonardo has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer, another Arduino, or other microcontrollers. The ATmega32U4 provides UART TTL (5V) serial communication, which is available on digital pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). The 32U4 also allows for serial (CDC) communication over USB and appears as a virtual com port to software on the computer. The chip also acts as a full speed USB 2.0 device, using standard USB COM drivers. On Windows, a .inf file is required. The Arduino software includes a serial monitor which allows simple textual data to be sent to and from the Arduino board. The RX and TX LEDs on the board will flash when data is being transmitted via the USB connection to the computer (but not for serial communication on pins 0 and 1).
A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the Leonardo's digital pins.
The ATmega32U4 also supports I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino software includes a Wire library to simplify use of the I2C bus. For SPI communication, use the SPI library.
The Leonardo appears as a generic keyboard and mouse, and can be programmed to control these input devices using the Keyboard and Mouse classes.
Programming
The Leonardo can be programmed with the Arduino software (download). Select "Arduino Leonardo from the Tools > Board menu (according to the microcontroller on your board). For details, see the reference and tutorials.
The ATmega32U4 on the Arduino Leonardo comes preburned with a bootloader that allows you to upload new code to it without the use of an external hardware programmer. It communicates using the AVR109 protocol.
You can also bypass the bootloader and program the microcontroller through the ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header using Arduino ISP or similar.
The Leonardo can be programmed with the Arduino software (download). Select "Arduino Leonardo from the Tools > Board menu (according to the microcontroller on your board). For details, see the reference and tutorials.
The ATmega32U4 on the Arduino Leonardo comes preburned with a bootloader that allows you to upload new code to it without the use of an external hardware programmer. It communicates using the AVR109 protocol.
You can also bypass the bootloader and program the microcontroller through the ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header using Arduino ISP or similar.
Automatic (Software) Reset
Rather than requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the Leonardo is designed in a way that allows it to be reset by software running on a connected computer. The reset is triggered when the Leonardo's virtual (CDC) serial / COM port is opened at 1200 baud and then closed. When this happens, the processor will reset, breaking the USB connection to the computer (meaning that the virtual serial / COM port will disappear). After the processor resets, the bootloader starts, remaining active for about 8 seconds. The bootloader can also be initiated by pressing the reset button on the Leonardo. Note that when the board first powers up, it will jump straight to the user sketch, if present, rather than initiating the bootloader.
Because of the way the Leonardo handles reset it's best to let the Arduino software try to initiate the reset before uploading, especially if you are in the habit of pressing the reset button before uploading on other boards. If the software can't reset the board you can always start the bootloader by pressing the reset button on the board.
Rather than requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the Leonardo is designed in a way that allows it to be reset by software running on a connected computer. The reset is triggered when the Leonardo's virtual (CDC) serial / COM port is opened at 1200 baud and then closed. When this happens, the processor will reset, breaking the USB connection to the computer (meaning that the virtual serial / COM port will disappear). After the processor resets, the bootloader starts, remaining active for about 8 seconds. The bootloader can also be initiated by pressing the reset button on the Leonardo. Note that when the board first powers up, it will jump straight to the user sketch, if present, rather than initiating the bootloader.
Because of the way the Leonardo handles reset it's best to let the Arduino software try to initiate the reset before uploading, especially if you are in the habit of pressing the reset button before uploading on other boards. If the software can't reset the board you can always start the bootloader by pressing the reset button on the board.
USB Overcurrent Protection
The Leonardo has a resettable polyfuse that protects your computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent. Although most computers provide their own internal protection, the fuse provides an extra layer of protection. If more than 500 mA is applied to the USB port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short or overload is removed.
The Leonardo has a resettable polyfuse that protects your computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent. Although most computers provide their own internal protection, the fuse provides an extra layer of protection. If more than 500 mA is applied to the USB port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short or overload is removed.
Physical Characteristics
The maximum length and width of the Leonardo PCB are 2.7 and 2.1 inches respectively, with the USB connector and power jack extending beyond the former dimension. Four screw holes allow the board to be attached to a surface or case. Note that the distance between digital pins 7 and 8 is 160 mil (0.16"), not an even multiple of the 100 mil spacing of the other pins.


배송안내
- 배송비 : 기본배송료는 3,000원 입니다. (도서,산간,오지 일부지역은 배송비가 추가될 수 있습니다) 70,000원 이상 구매시 무료배송입니다.
- 본 상품의 평균 배송일은 3~4일입니다.(입금 확인 후) 설치 상품의 경우 다소 늦어질수 있습니다.[배송예정일은 주문시점(주문순서)에 따른 유동성이 발생하므로 평균 배송일과는 차이가 발생할 수 있습니다.]
- 본 상품의 배송 가능일은 3~4일 입니다. 배송 가능일이란 본 상품을 주문 하신 고객님들께 상품 배송이 가능한 기간을 의미합니다. (단, 연휴 및 공휴일은 기간 계산시 제외하며 현금 주문일 경우 입금일 기준 입니다.)
교환 및 반품안내
- 상품 택(tag)제거 또는 개봉으로 상품 가치 훼손 시에는 상품수령후 7일 이내라도 교환 및 반품이 불가능합니다.
- 저단가 상품, 일부 특가 상품은 고객 변심에 의한 교환, 반품은 고객께서 배송비를 부담하셔야 합니다(제품의 하자,배송오류는 제외)
- 일부 상품은 신모델 출시, 부품가격 변동 등 제조사 사정으로 가격이 변동될 수 있습니다.
- 개별 주문제작상품의 경우에는 제작완료, 인수 후에는 교환/반품기간내라도 교환 및 반품이 불가능 합니다.
환불안내
AS안내
- 소비자분쟁해결 기준(공정거래위원회 고시)에 따라 피해를 보상받을 수 있습니다.
- A/S는 판매자에게 문의하시기 바랍니다.
이미지 확대보기
아두이노 레오나르도 정품 Arduino Leonardo / 헤더 포함

비밀번호 인증
글 작성시 설정한 비밀번호를 입력해 주세요.
확인장바구니 담기
상품이 장바구니에 담겼습니다.
바로 확인하시겠습니까?